Keep your files and folders secure
Your Mac contains files and folders where you keep personal data and documents. To protect your files and keep them secure from prying eyes, you can use a password or other means of encrypting the files, but there’s a default way that’s built into macOS for that.
Disk permissions (or directory permissions) on macOS are designed to prevent other users and certain programs from opening files on your Mac and modifying them without permission. This way, you can rest easy knowing your files and folders are secure.
If you’re having trouble with disk permissions on your Mac, this guide explains how to fix or repair disk permissions in macOS.
What Are Permissions in macOS and How Do They Work?
Permissions in macOS control the user accounts that can access the files or folders on your Mac. You can change the permission settings in Finder at the bottom of the Info window for a file, folder, or disk.
For example, you can change folder permission settings such that other users on your Mac who connect to it for file sharing can only view but not modify the files in the folders.
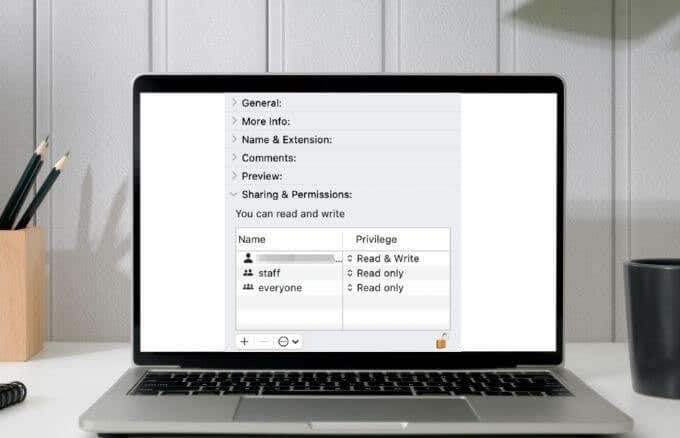
The permissions, which consist of read, write and execute activities, can be edited by three types of users: the owner, a group, and everyone using the computer.
As the owner of the computer, you can use permissions to define separate rules for yourself, a group, or every user. These permissions include file or folder sharing, file access rights, and system integrity.
How to View File System Permissions on macOS
Viewing file system permissions isn’t limited to the owner of the computer. Anyone else can view the file and folder permissions through the Finder app’s Info window as well.
To see permissions of a file or folder:
- Right-click the file or folder and select Get Info from the context menu.
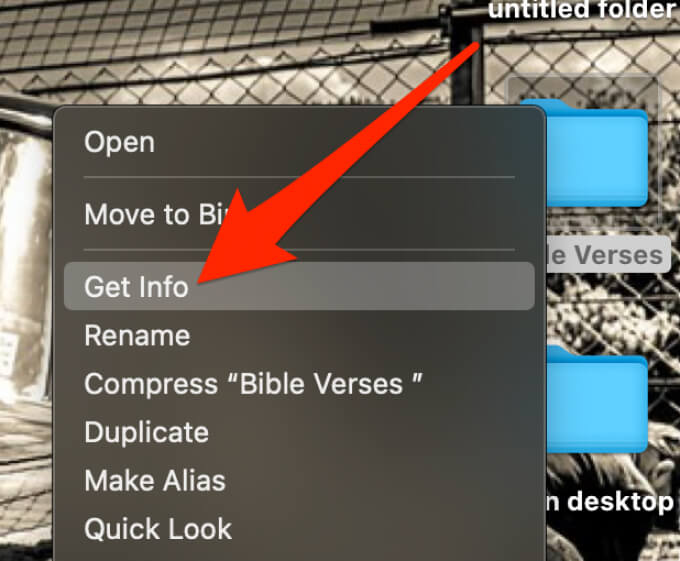
- Select Sharing & Permissions to expand the permissions.
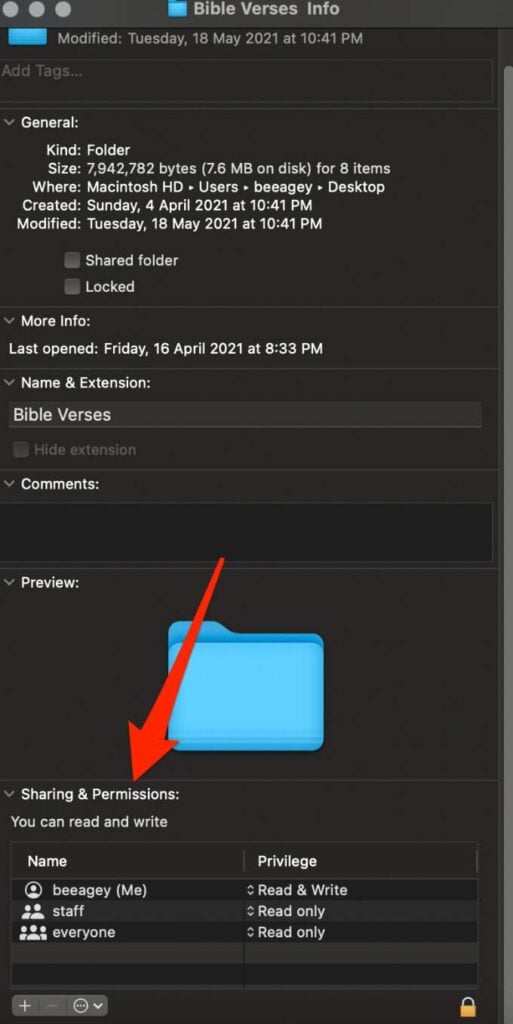
- You’ll find three different types of users in the permission fields: Owner, group, and everyone.
- Owner: The creator of the item or the person who copied it to the computer.
- Group: A set of joined user accounts whose permissions apply to all members.
- Everyone: Defines access for anyone including guest, local, and sharing users.
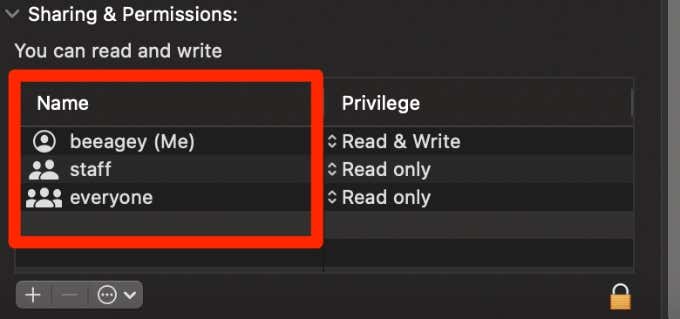
- Next to each user account, you’ll see permissions such as Read, Read and Write, Execute, or No access.
- Read permissions: Allow the user or group members only to open a file or browse a list of items in a folder. They cannot save any changes to the file or folder.
- Write permissions: Allow the user or group members to modify or delete the file or folder.
- Execute permissions: For a file, this means the user can execute the file if it’s a script or program. Files that aren’t a script or program shouldn’t have the execute permission enabled. For a folder, it means the user can open the folder and see the files so long as the read permission is enabled.
Why You Should Repair Disk Permissions in macOS
The files and folders on your Mac each have an associated set of permissions. In addition, most of the things you install on your Mac are installed from package files, which also store other files that don’t take up too much space on your hard disk.
Within the package file are Bill of Materials files (.bom), which contain a list of files that the package has installed and the permissions for each file.
However, these file permissions can be modified, especially when you’re installing and uninstalling apps on your Mac. When the permissions are affected, programs on your Mac may alter and modify files, which could end up causing all sorts of system issues like freezing, lagging or crashing, and permission errors.
If you notice some strange changes in your Mac’s performance or apps aren’t working right, you should start by troubleshooting the disk permissions.
Fortunately, if your Mac is running macOS Mojave 10.14 or newer versions, any new apps added to your Mac will ask for permission to use some features. If you deny these permissions, the apps may not function properly, but it increases privacy and security for your data.
Fixing or repairing disk permissions in macOS ensures that your operating system can access or modify particular files. For example, disc permissions ensure that you can start up your Mac, log into your account, print or launch apps, and more.
Repairing disk permissions on macOS also ensures that particular files have the right permissions to prevent unauthorized access by apps or users that shouldn’t be meddling with those files.
How to Fix or Repair Permissions in macOS
Repairing permissions is a standard Mac troubleshooting tip that appears to solve many rare types of problems on macOS. However, the option disappeared from the Disk Utility app after the release of OS X El Capitan 10.11.
Apple replaced the feature with System Integrity Protection (SIP), which prevents potentially malicious software from accessing important files on your computer.
You can still repair disk permissions in macOS as the option is now part of First Aid, which bundles several actions together that resolve different issues related to the disk drive.
Here’s how to check and repair the disk volume for any errors:
- Select Go > Utilities > Disk Utility to open Disk Utility.
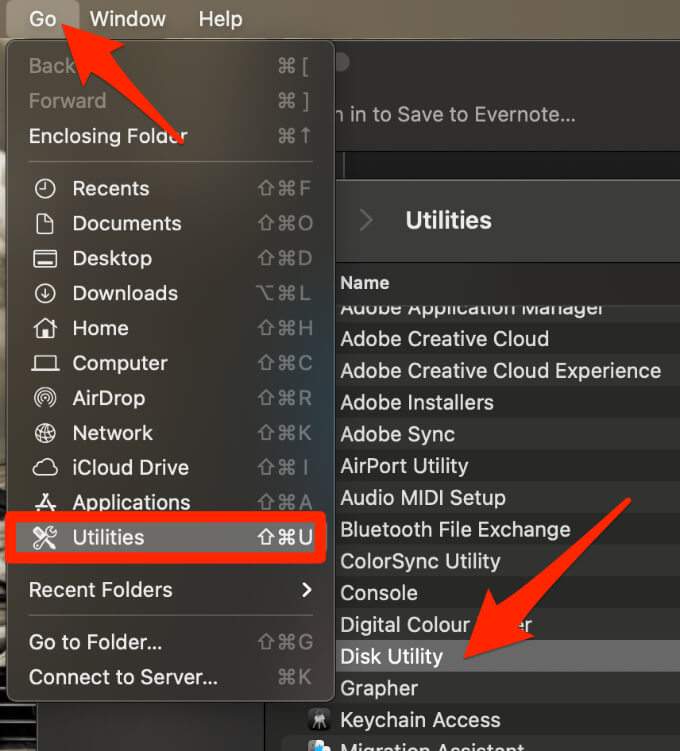
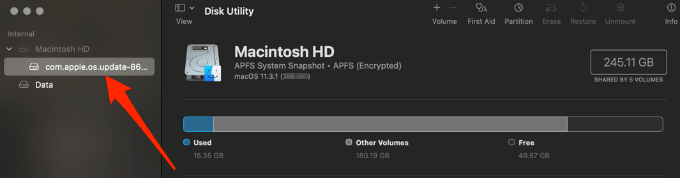
- Next, select your boot volume in the left pane.
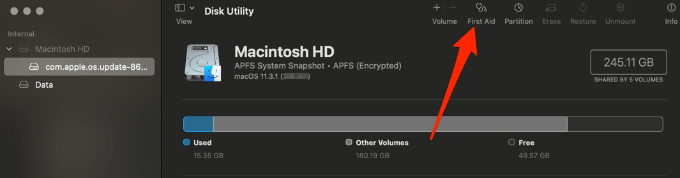
- Select First Aid in the Disk Utility toolbar at the top right side of the window.
- Confirm that you selected the right drive, and then select Run to start the disk repair process. Select Continue if you get in the warning message popup.
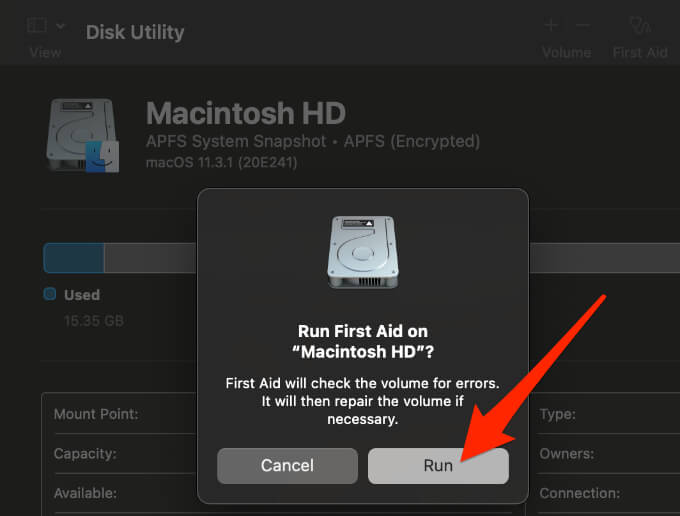
While the repair process is in progress, your Mac won’t respond to any input, which is normal and expected. This happens because macOS needs to analyze the drive’s contents correctly but it won’t take more than a few minutes to complete.
Once the repair process is completed, you’ll get a report that displays everything the process accomplished. If there are any serious errors, you’ll be notified of the issues it finds.
Reset Permissions for the Home Folder
The Home folder on your Mac is your user folder, which contains several other folders you access frequently like Desktop, Applications, Documents, Downloads, and more.
Here’s how to reset permissions for the Home folder to repair disk permissions.
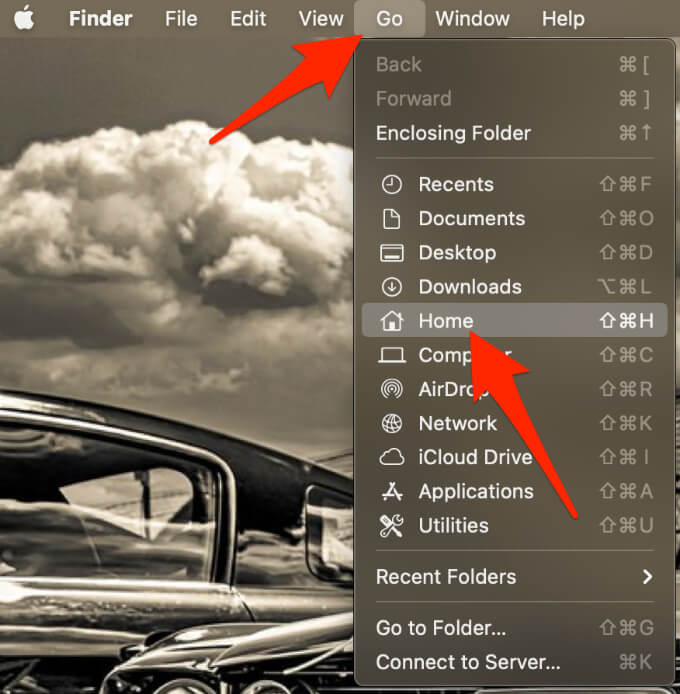
- Select Go > Home.
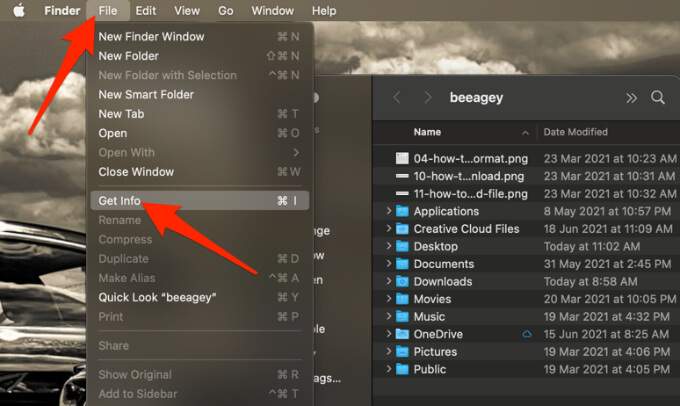
- Next, select File > Get Info.
- Select Sharing & Permissions to view the folder’s permissions. If the Sharing & Permissions section isn’t open, select the arrow to expand it.
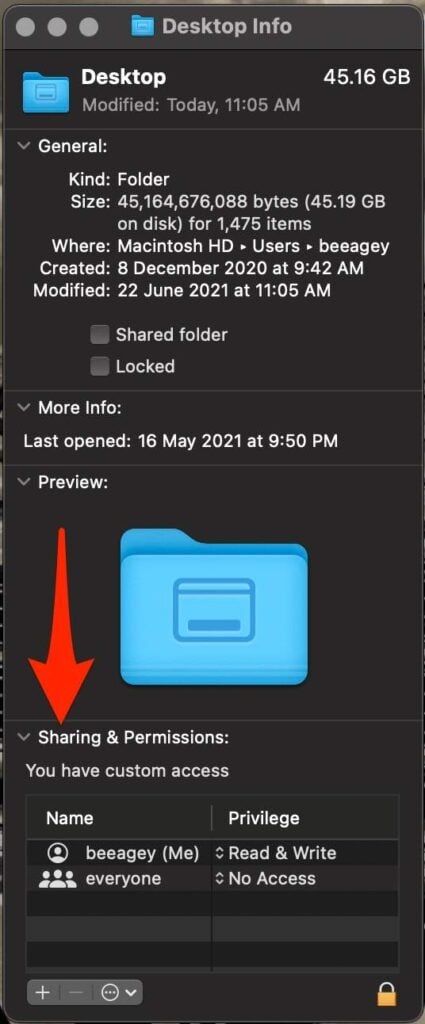
- Next, select the Lock button.
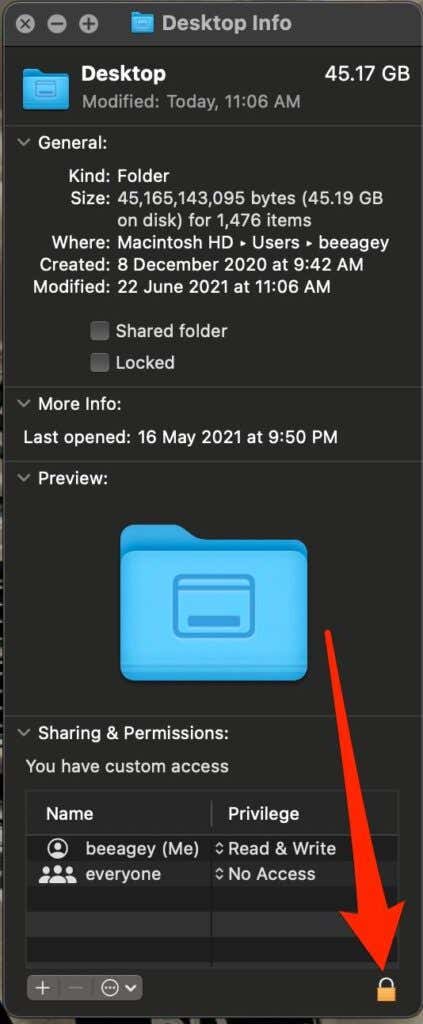
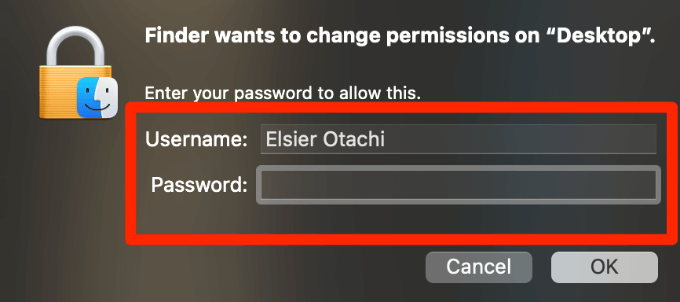
- Enter your admin name and password.
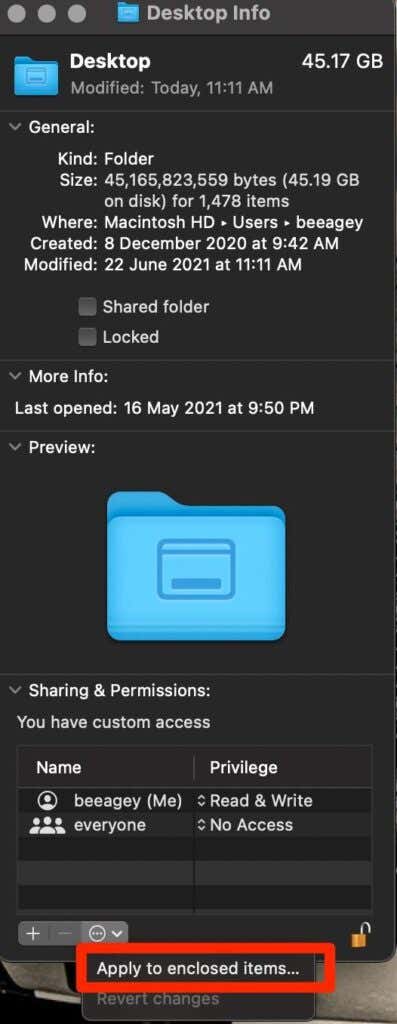
- Select the Action menu > Apply to enclosed items.
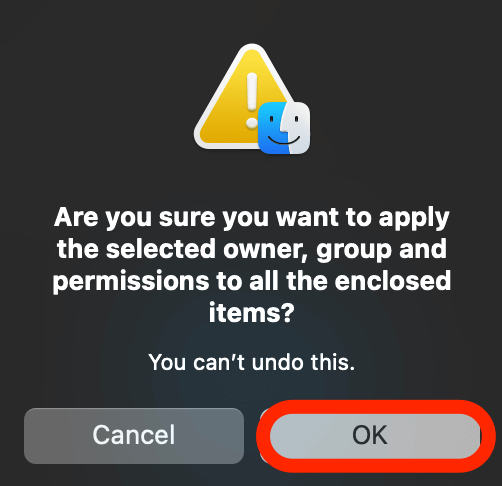
- Next, select OK to complete the permissions reset process. A progress bar will appear at the top of the window and the changes will be reflected throughout the Home folder.
- Once the progress bar completes, select Go > Utilities > Terminal to open Terminal.
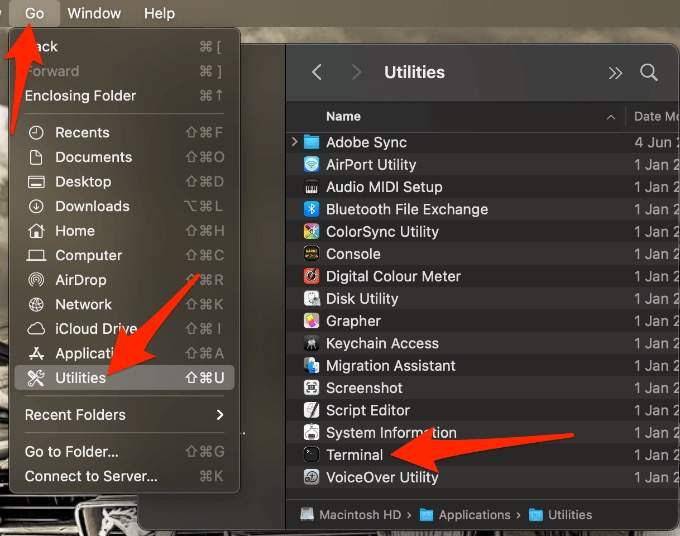
- Type or paste this command: diskutil resetUserPermissions / ` id -u` to reset permissions on the root volume (/) to the current user ID.
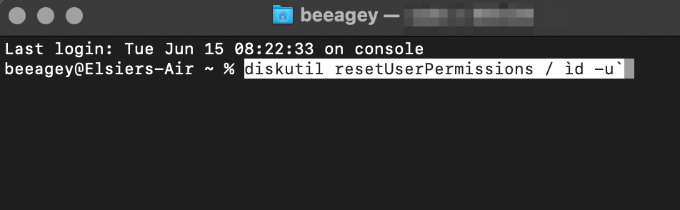
- When the process completes, quit Terminal, and restart your Mac to effect the changes.
What to Do If You Get the Error 69841 While Resetting Permissions on a Mac
Sometimes resetting the user permission on the root volume may not go as planned. You may get the “error 69841 permissions reset on user home directory failed” message. If you get this error, here’s what to do depending on your macOS version.
On macOS Mojave or newer versions
- Select Apple menu > System Preferences > Security & Privacy.
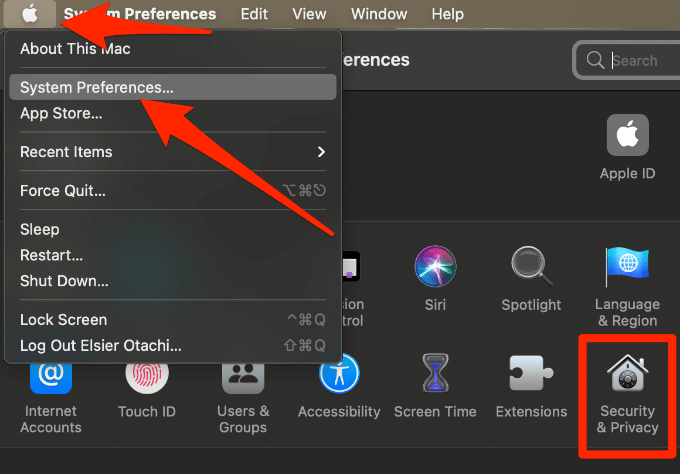
- Next, select the Privacy tab, select the Lock icon and enter your admin name and password.
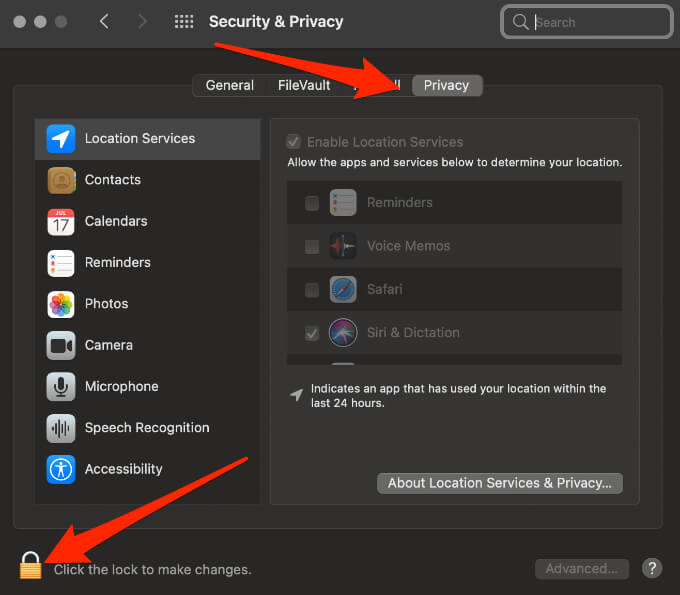
- Select the Full Disk Access tab and then select the Add (+) button.
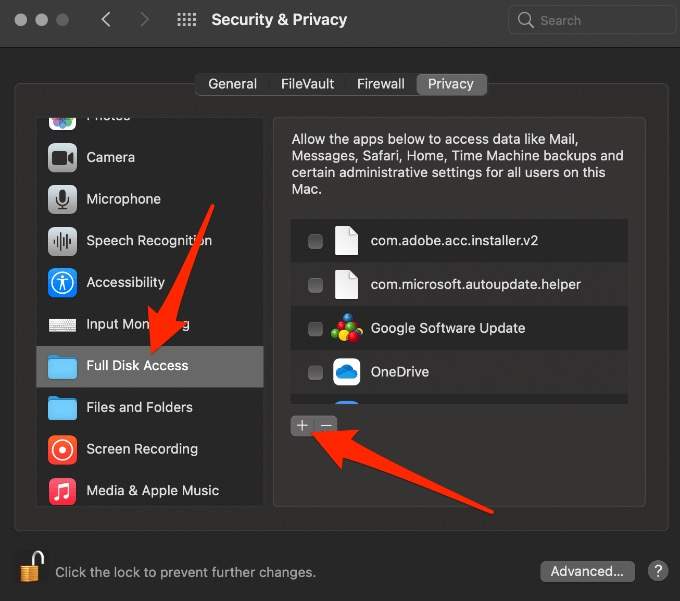
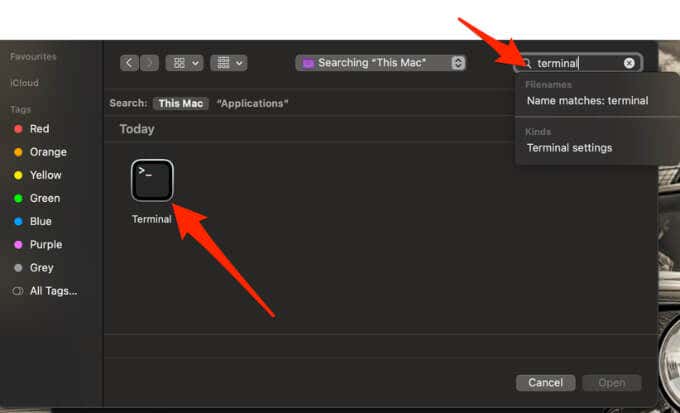
- Search for Terminal and add it to Full Disk Access.
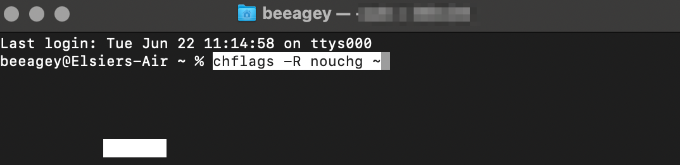
- Open Terminal and paste or type this command: chflags -R nouchg ~. Press Return.
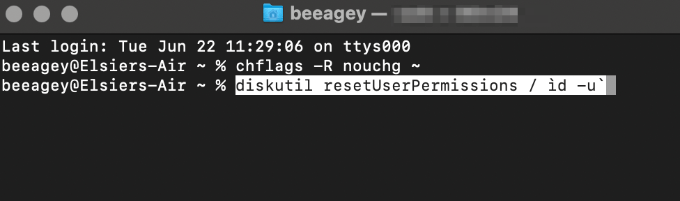
- Next, type diskutil resetUserPermissions / `id -u` and press the Return key.
- Restart your Mac to effect the changes.
On macOS High Sierra or Earlier Versions
Unlike macOS Mojave or later versions, you don’t need to add Terminal to Full Disk Access in macOS High Sierra or earlier versions before resolving the error 69841 on your Mac.
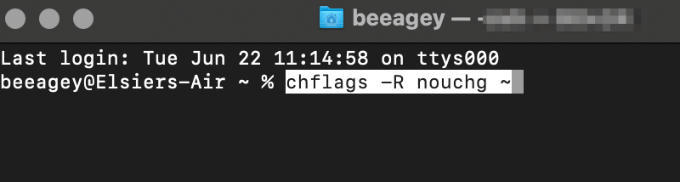
- Open Terminal and enter chflags -R nouchg ~.
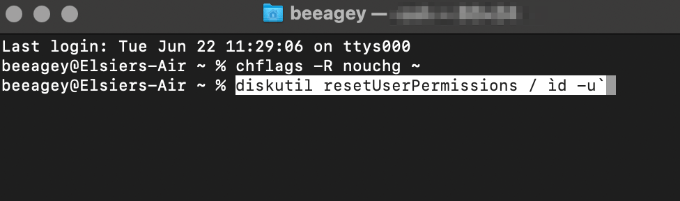
- Next, type diskutil resetUserPermissions / ìd -u` and press Return.
- Restart your Mac to effect the changes.
Keep Your Mac in Good Shape
Fixing or repairing disk permissions in macOS should be done only if you suspect that you have file or folder permission issues, especially if you install and delete software frequently. That said, you need to be careful about the software you download to your computer.
We have other guides that can help you fix issues with your Mac such as when Bluetooth isn’t working on your computer, Mac camera isn’t working or your Mac won’t go to sleep.
Were you able to fix or repair disk permissions using the steps in this guide? Tell us about it in a comment below.